Address
1160/61, University Rd, Revenue Colony, Shivajinagar, Pune, Maharashtra 411005
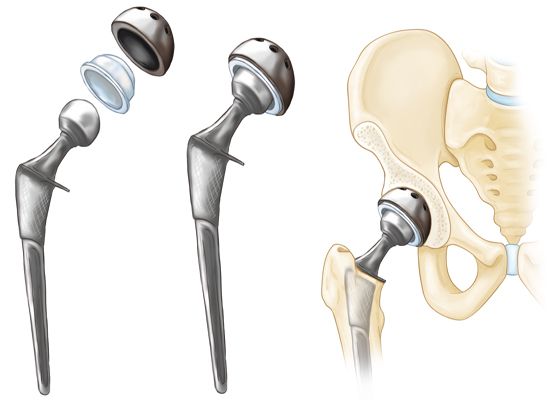
Total hip replacement is advised by doctor when both acetabulum (cup of hip joint) and femoral head (Ball of hip joint) are damaged and there articular surfaces are no longer smooth. Common disease where total hip replacement is needed includes Avascular necrosis of femoral head, rheumatoid arthritis, acetabulum fracture, femoral neck and head fracture, arthritis etc.
The Direct Anterior Approach is a modern, minimally invasive technique for (THR) total hip replacement surgery. This method provides direct access to the front of the hip, offering advantages like quicker recovery, fewer hip precaution and a reduced risk of implant dislocation. Orthopedic surgeons widely adopt DAA for its benefites over traditional hip replacement approaches.
Regular Approach :
Anterior Approach :

This approach provides direct access to the front of the hip. Surgeons like it for fixing hip fractures. It's versatile and can handle periprosthetic fracture too.
Hip replacement surgery becomes a viable option for individuals facing various conditions that affectthe hip joint. This includes :
| OPEN PROCEDURE | MINIMALLY INVASIVE PROCEDURES | |
|---|---|---|
| Scars & Stitches | BIG | MINIMAL |
| Muscle & Tendon Cuts | HIGH | LOW |
| Post-Operation Pain | HIGH | LOW |
| Infection Chances | HIGH | VERY LOW |
| Hospital Duration | LONG | SHORT |
| Recovery Period | VERY HIGH | LOW |
Why risk permanent immobility? Delaying hip replacement surgery may lead to severe consequences such as bedridden conditions, ineligibility for future operations and increased risks of injuries. Act now to regain control of your life.
Hip arthroplasty, or hip replacement, is a surgical procedure addressing hip joint pain by replacing parts with artificial implants. Indications include injuries, osteoarthritis and femoroacetabular impingement syndrome.
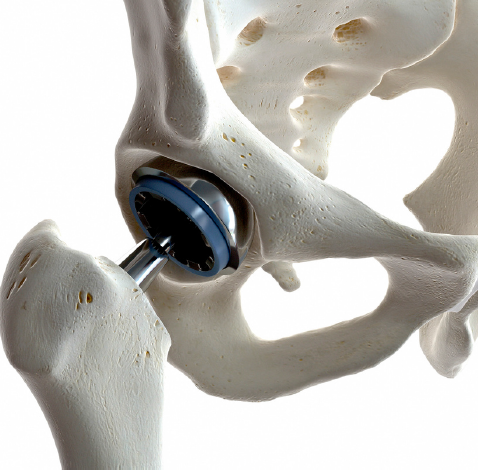
The choice of implant material depends on factors such as age, activity level, and the specific condition of the patient
1. Metal-on-Plastic : Involves a metal ball and a plastic socket. Commonly used for its durability and suitability for a wide range of patients.
2. Ceramic-on-Plastic or Ceramic-on-Ceramic: Utilizes a ceramic ball with a plastic socket or both ceramic components. Often preferred for younger, more active patients due to its wear resistance.
3. Oxanium on Plastic: Combines an Oxinium head with a plastic socket. This option is chosen for its durability and potential advantages in specific patient cases.